Estimating concrete costs accurately is crucial for any construction project. Understanding the factors that affect these costs and learning effective calculation methods can help you plan better and stay within budget. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to estimate concrete costs efficiently.
To estimate concrete costs, start by determining the volume of concrete needed for your project. Then, calculate the total cost by determining the prices of materials, labor, and equipment. Consider additional expenses such as permits, taxes, and any special requirements. Finally, review and adjust your estimate based on market fluctuations and any unforeseen circumstances that may arise during construction.

Factors Affecting Concrete Cost
Many factors will need to be considered, including the kind of concrete mix, location of the project, accessibility of the construction site, size of the project, and specific design requirements. The overall cost of concrete can also be affected by factors such as labor costs, market demand, and the price of raw materials.
Concrete Type and Its Impact on Price

The type of concrete you choose significantly influences the overall cost. Different types of concrete are suited for various applications, each with unique properties and price points. Here are some common types:
- Standard Concrete: Ideal for general construction projects, it’s the most affordable option.
- HighStrength Concrete: Used in demanding structures like bridges and highrise buildings, it’s more expensive due to its enhanced durability.
- Stamped or Decorative Concrete: Adds aesthetic value to driveways and patios, but comes at a premium due to additional labor and materials.
- Reinforced Concrete: Essential for heavy loadbearing structures, it includes steel reinforcement which increases the cost.
Understanding the specific requirements of your project will help you choose the right type of concrete, balancing performance with budget.
Labor Costs
Labor costs are a significant part of concrete expenses. Skilled labor is required for tasks such as mixing, pouring, and finishing the concrete. The complexity of the project, local labor rates, and the time required for completion can all affect labor costs.
Site Preparation
Preparing the site for concrete pouring involves clearing the area, leveling the ground, and installing forms. These preparatory steps can add to the overall cost, especially if extensive work is needed to make the site ready.
Transportation and Delivery
The cost of transporting concrete to your site can vary based on the distance from the supplier and the accessibility of the location. Delivery charges can significantly impact the total cost, especially for large projects or sites in remote areas.
Concrete Cost Calculation Methods
A computerized cost calculation system offers several benefits over traditional manual methods. Firstly, it reduces the chances of human error, ensuring more accurate and reliable cost calculations. Additionally, it saves time and effort by automating the process, allowing for faster and more efficient calculations. Finally, it provides a centralized and organized platform for storing and accessing cost data, making it easier to track and analyze expenses.
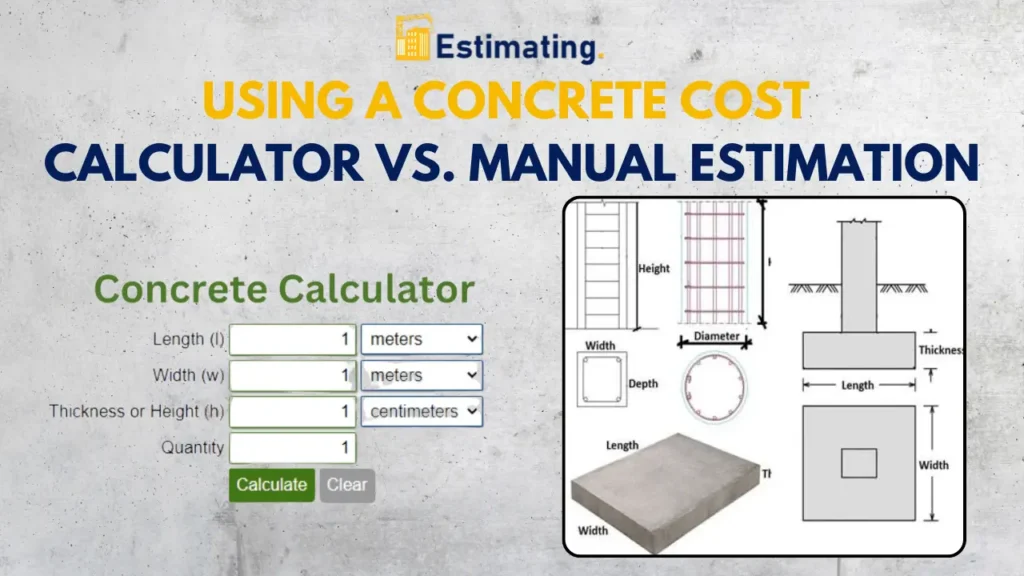
Using a Concrete Cost Calculator vs. Manual Estimation
There are two primary methods to estimate concrete costs: using an online concrete cost calculator or performing a manual estimation.
Concrete Cost Calculator:
- Convenience: Simply input the dimensions of your project (length, width, and depth), and the calculator provides an instant estimate.
- Accuracy: Calculators often include factors like wastage and variations in concrete mix ratios, offering a more precise estimate.
- TimeSaving: Quickly generates cost estimates, ideal for preliminary budgeting. You can find an example of a concrete cost calculator here.
Manual Estimation:
Allows for custom adjustments based on specific project needs.
Steps:
- Measure the area where concrete will be poured.
- Calculate the volume (length x width x depth).
- Convert the volume to cubic yards (or meters).
- Determine the cost per cubic yard (or meter) based on the type of concrete.
- Add additional costs like labor, reinforcement materials, and delivery.
Manual estimation requires more effort but provides a deeper understanding of cost breakdowns. For more insights on the construction estimating process, visit here.
Additional Costs to Consider

The unit cost method is a valuable tool for calculating the cost of a concrete project. It allows for accurate estimation by breaking down the project into individual components and assigning costs to each unit. This method provides transparency and helps identify areas of potential cost savings or adjustments in the project plan.
Permits and Inspections
Depending on your location and the scope of your project, you may need to obtain permits and pass inspections. These can add to your overall costs and should be factored into your budget from the start. For more information on permits, visit this site
Finishing and Sealing
After the concrete is poured and set, additional costs may arise from the finishing and sealing processes. These steps ensure the durability and aesthetic quality of the concrete but can increase the total expense.
Tips for Reducing Concrete Costs
Alternative materials like fly ash or slag can replace a portion of cement, mix design can be optimized to reduce cement use, and planning and coordinating the construction process can reduce waste and rework. In addition to precast concrete components, you can also consider using them, which can be manufactured off-site, transported, and installed faster and cheaper.
Seasonal Discounts and Bulk Ordering
Effective cost management can lead to significant savings on concrete purchases. Here are some strategies:
- Seasonal Discounts: Concrete suppliers often offer discounts during off peak seasons (late fall to early spring). Planning your project around these times can reduce material costs.
- Bulk Ordering: Purchasing larger quantities can lower the price per unit. Buying in bulk can result in substantial savings if you have multiple projects or future needs.
- Local Suppliers: Choosing local suppliers can reduce delivery fees and support local businesses, potentially leading to better deals.
- Mix Adjustments: For less critical parts of your project, consider using a less expensive mix or a mix with more aggregate.
Avoiding common construction estimating mistakes can also help in reducing costs. For a list of common mistakes and how to avoid them, check out this guide.
Conclusion
You can effectively estimate and manage your concrete expenses by understanding the factors that affect concrete costs, utilizing accurate calculation methods, and employing cost-saving strategies. This comprehensive approach ensures your construction project is both financially sound and successful. Proper planning and smart purchasing decisions can significantly reduce overall costs, making your project more efficient and economical.
For more detailed insights on concrete costs and management, visit Concrete Network. To learn more about construction estimating and its importance, explore this article.






